Tornadoes
Nature's scariest colums of windy death
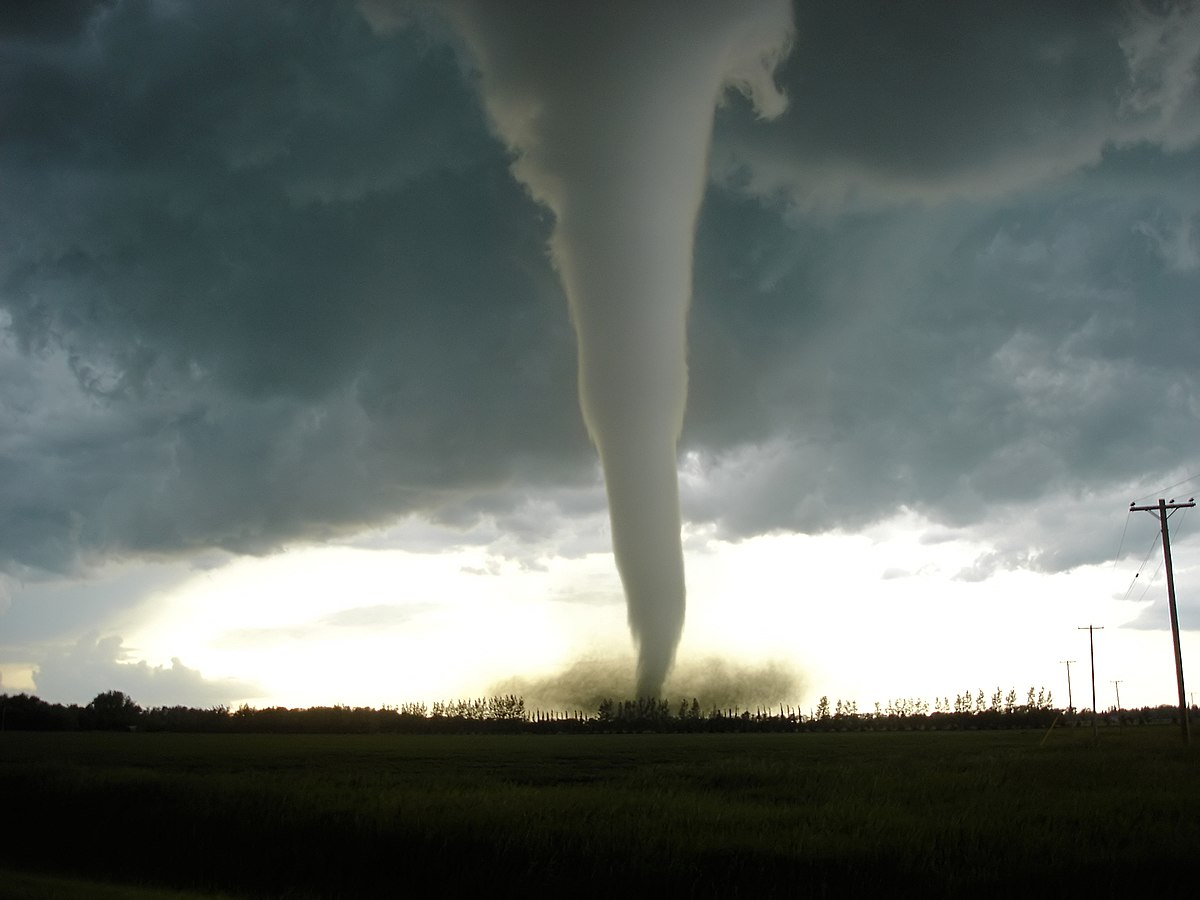

What is a Tornado?
A tornado is a violently rotating column of air that extends from a thunder storm [or super cell] and comes into contact with the ground.
Tornadoes require several different ingredients to form in the perfect conditions. Those conditions are:
- Warm Moist Air to collide with cooler dry air and rises to form a supercell
- Instability in the atmosphere, which must be cooler then the rising air
- Time
- Wind Shear
- Forward and Rear Flank Downdrafts (FFD/RFD)
The Generation
Tornadoes form during a thunderstorm where the upper and lower wind shears work together to cause a horizontal rotation.
Heavy rain fall causes the Front Flank Downdraft (FFD) to move forwards and backwards, and in cooperation with the Rear Flank Downdraft,
they push the horizontal rotation to become more vertical rotation.
The beginning of the development stage, where some circulations are visible near the supercell cloud base. The next stage after is the Mature stage, where the tornado
is at it's most violent and dangerous stage. Sometimes, when a mature tornado has insufficient moisture in the air, the funnel wouldn't be visible, but a lively tornado could
still be on the ground. An easy indiction to tell if a tornado is present is the rotating debris and dust that gets kicked up by the tornado.
Finally, the last stage of a tornado, the Dissipating stage. In this stage, the tornado ends its line of destruction and begins to dissipate. The RFD cuts of the circulation of the storm and
destroys the rotation of the storm itself.
Enhanced Fujita Scale (EF Scale)
The EF Scale is the bigger and better brother to the F scale. The Fujita Scale was introduced in 1971 and until 2007 was widely used to rate tornadoes.
In the United States, on February 1st, 2007, the EF scale sought to fix the accuracy the F scale couldn't achieve [moreso being up to date].
The EF scale made some changes to the wind speeds, and more accurately accounted for new damaged like man-made or natural structures.
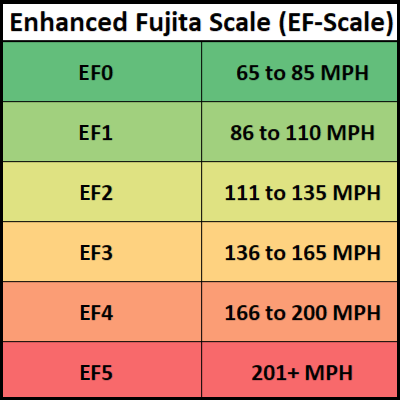
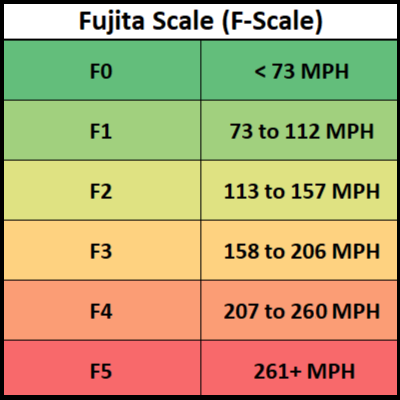
Left: Enhanced Fujita Scale wind speeds; Right: Fujita Scale wind speeds
Facts / Records
The main area of Tornadoes are a location in the United States named Tornado Alley, where a good majority of Tornadoes occur, especially in the US.
Tornadoes have been recorded to occur everywhere in the world besides Antarctica.
- In the US alone, there are 71 deaths a year by tornadoes
- The longest tornadeo was the Tri-State Tornado (1925)
- The biggest death count was 695 killed in one tornadeo
- The highest count of tornadoes in a single year is 2004 with 1,817
- Wisconsin Records
- Averages 23 tornadoes per year
- 2 EF5 tornadoes in the past 70 years
- Oakfield Tornado (July 18th, 1996), 12 people were injured, causing $40.4 million in damages
- Barnevald Tornado (June 8th, 1984), 9 were killed, 200 injured, causing $40 million in damages
Safety
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/CFBLKX5HK5JE3CV2MBZ5TQYBR4.jpg)
Damages to a house during a tornado at the Missouri capital.
During a Tornado Watch, you may still do your daily routine and tasks that you wished to do, just be alert and ready. A Tornado Watch means there are meteorlogical conditons favourable for a severe thunderstorm capable of producing a Tornado.
The threat is not confirmed, but the effected area should stay alert and look for warning sides outside.
During a Tornado Warning, however, SEEK SHELTER IMMEDIATELY. There is a reported tornado on the ground or confirmed by radar.
Go to the lowest floor and in a secluded room, no windows, door closed. If there is a staircase, get under it. It is usually the most structurely sound place in the house.